Back>Cotton
Cotton is a major crop of Pakistan after wheat and it occupies the largest area in Pakistan compared to other crops. Cotton crop earns the country largest export revenues and in addition to the lint, the seed of cotton for oil and meal accounts for 80 percent of the national production of oilseed.



Bemisia tabaci
سفید مکھی
COTTON
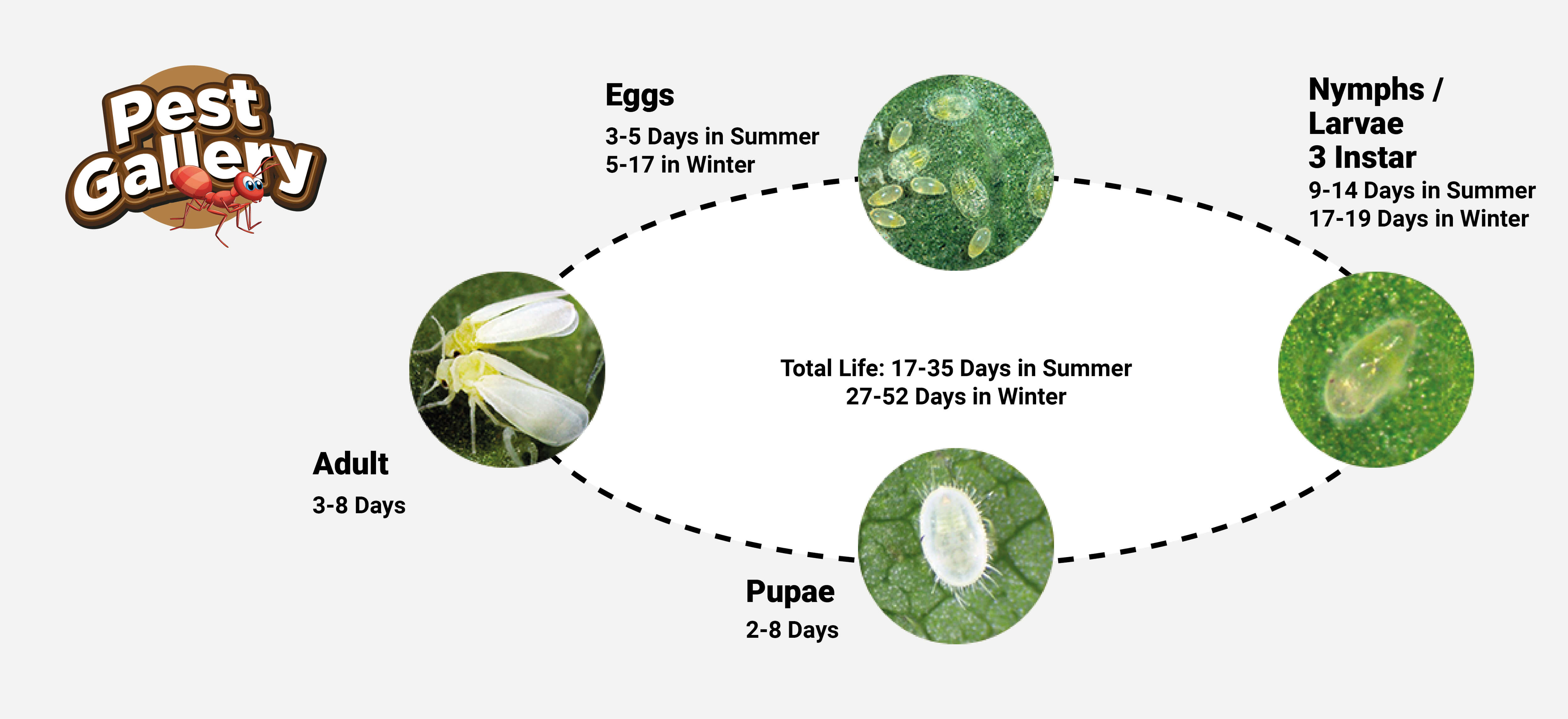
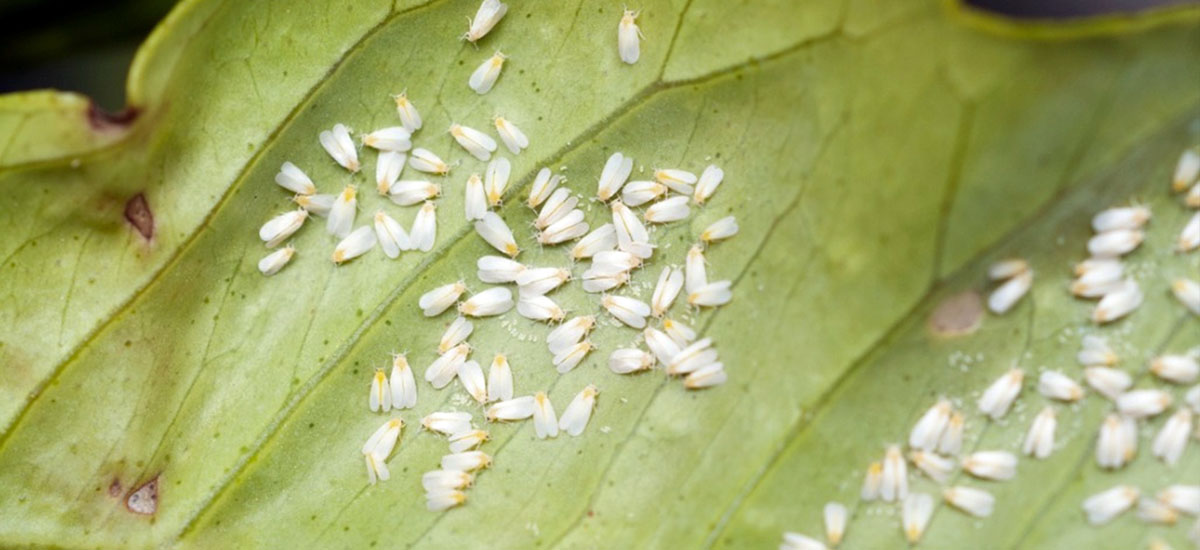
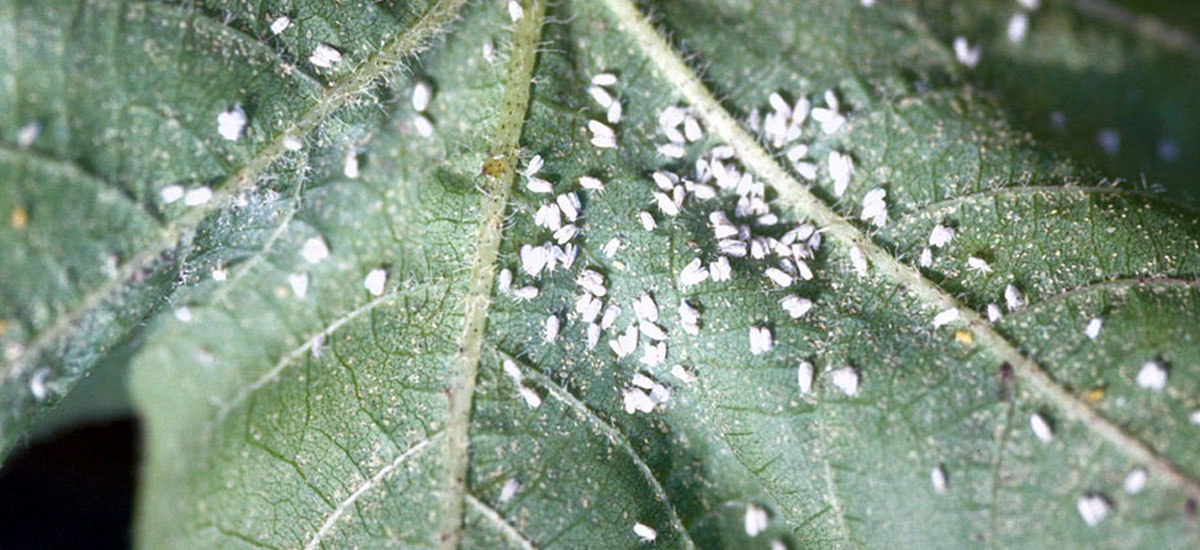
Whitefly is a serious pest of cotton that lowers yield by feeding on the underside of the leaf and spreading diseases like Cotton Leaf Curl Virus. Whiteflies feed on the sap of the leaves and release a fluid on to the leaves on which a black fungus grows. This affects photosynthesis, the food making process of the plant, and so lowers the strength of the plant.
Bemisia tabaci
سفید مکھی
COTTON
ETL: 5 per Leaf

Bemisia tabaci
سفید مکھی
COTTON
Whitefly cause damage to cotton plants in two ways, firstly by sucking the sap and secondly by excreting honey dew on which sooty mould grows. Damage from direct feeding reduces the photosynthesis activities of the plant and hence the yield. Indirect damage results from lint contamination with honey dew and associated fungi and through transmission of leaf curl virus disease. Late season severity affects seed development and lint quality.

.jpg)

.jpg)
Dysdercus cingulatus
ریڈ کاٹن بگ
COTTON
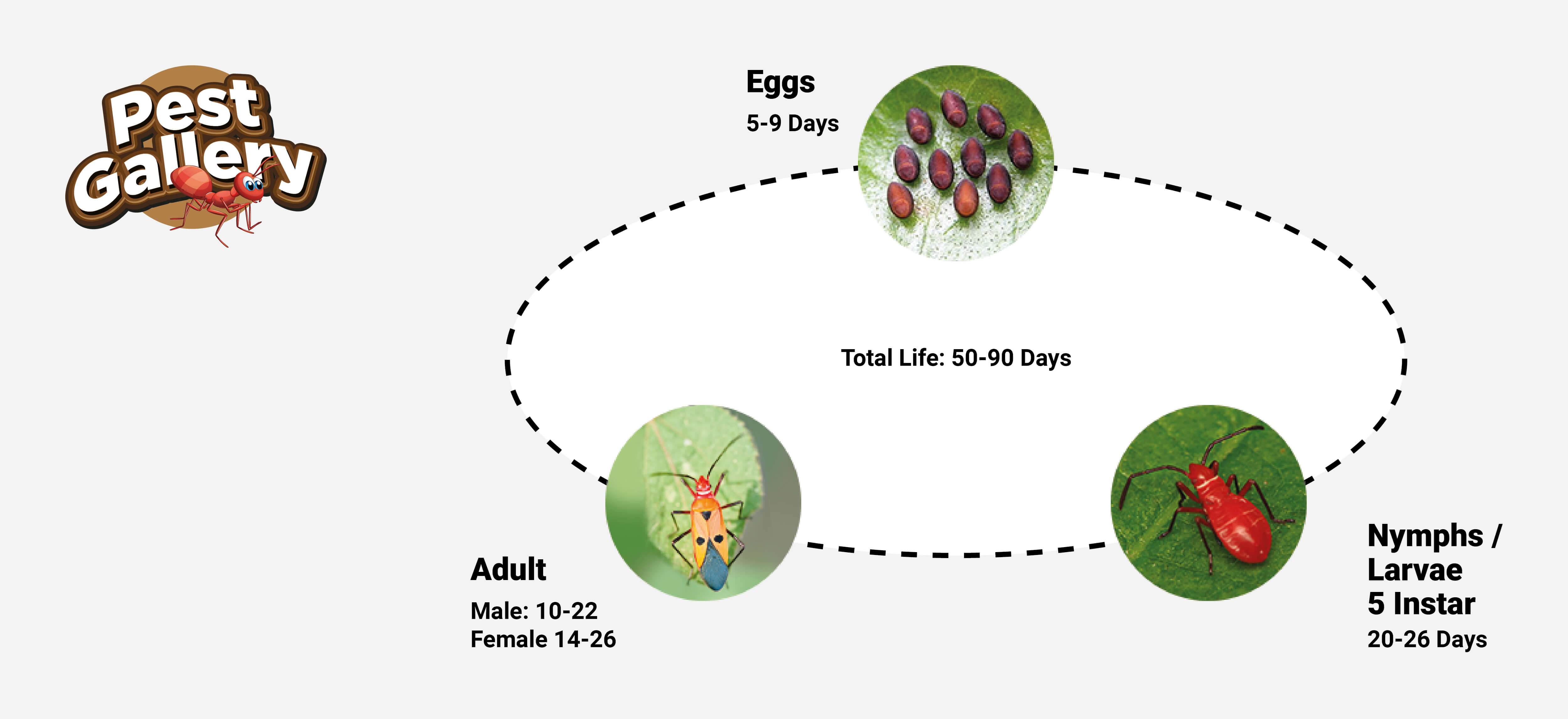
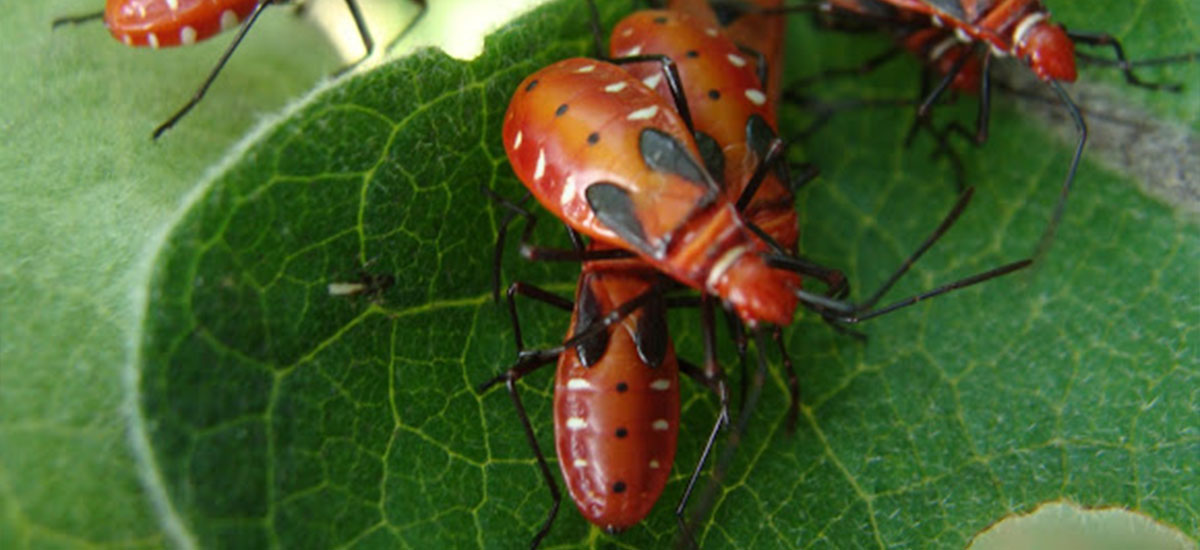
It is an occasional pest of cotton crop, the adults and older nymphs feeding on the emerging bolls and the cotton seeds as they mature, transmitting cotton-staining fungi as they do so.
Dysdercus cingulatus
ریڈ کاٹن بگ
COTTON
ETL: 15 (adult or nymph or collectively) per plant

Dysdercus cingulatus
ریڈ کاٹن بگ
COTTON
Adults and nymphs suck the sap from leaves, green bolls and seeds of partially opened bolls. Vitality of the plant is lowered, in general. Affected bolls open badly with their lint stained with the excreta or body juices. Quality of lint is affected and the attacked seed become unfit for either sowing or oil extraction. Boll rot is caused by secondary infection due to bacteria wherein rotting of the entire contents of the boll occur following the initial discoloration of the lint to yellow or brown.
.jpg)


.jpg)